Migraine is one of the most disabling neurological disorders, affecting approximately 11% of the world’s population. With frequent attacks of headache, this condition significantly impacts the quality of life of sufferers. But did you know that nutrition plays a crucial role in migraine prevention and treatment? In this article we explore how certain nutritional supplements may alleviate migraine symptoms and improve well-being.
Factors that Increase Migraine Frequency
Low or insufficient levels of essential nutrients may aggravate the severity and frequency of migraine attacks. In particular, oxidative stress and inflammation play a key role. These promote the secretion of inflammatory cytokines, such as tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-a, which in turn induce neuroinflammation and increase cell permeability, triggering migraine episodes.
The Role of Nutrients in Migraine
Research highlights a direct association between migraine attacks and a number of physiological factors, including:
- Mitochondrial disturbances.
- Disruptions in brain energy metabolism.
- Elevated levels of glutamate and homocysteine.
- activation of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP).
Based on these observations, nutrients that improve mitochondrial function and brain metabolism may alleviate migraine attacks.
Beneficial Nutritional Supplements
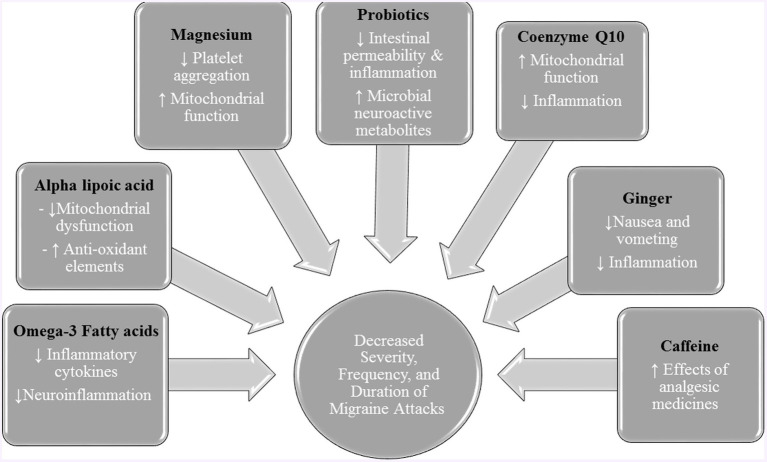
The following supplements have been shown to have favourable effects in reducing the frequency and intensity of migraines:
- Riboflavin (Vitamin B2): Supports mitochondrial function and reduces the frequency of attacks.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Known for their anti-inflammatory properties, they help mitigate inflammatory migraine triggers.
- Alpha Lipoic Acid: A potent antioxidant that fights oxidative stress.
- Magnesium: Improves muscle relaxation and prevents spasms associated with migraine.
- Probiotics: Help balance the gut-brain axis, which may reduce attacks.
- Coenzyme Q10: Improves cellular energy production and reduces symptoms.
- Ginger: With anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties, it is an effective natural solution.
- Caffeine: Can act as a vasoconstrictor, relieving headaches in some cases.
Conclusions
The scientific evidence supports the use of these supplements as promising tools in migraine management. However, further studies are essential to assess the impact of other nutrients on patients with this condition.
Adopting an appropriate nutritional strategy could make a difference in the lives of migraine sufferers.
Available in: Hajhashemy, Z., Golpour-Hamedani, S., Eshaghian, N., Sadeghi, O., Khorvash, F., & Askari, G. (2024). Practical supplements for the prevention and treatment of migraine attacks: a narrative review. Frontiers in Nutrition, 11, 1433390. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2024.1433390